 |
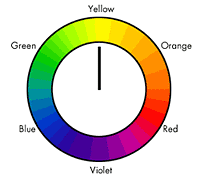
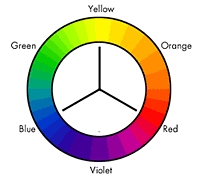
| Fig. 1 - The Itten Color Wheel |
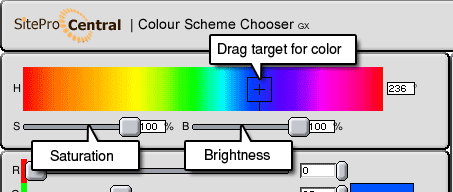
The color scheme chooser (GX) is based on classic color theory pioneered by Johannes Itten in the mid 1900s. Johannes Itten developed a new kind of color wheel that changed the way color was seen. This wheel is still in use today.
This tool is based on the Johannes Itten wheel which uses yellow, red and blue as it's primary colors. (see Fig.1)
Red, yellow and blue are mixed to create the secondary colors.
- Yellow and blue makes Green.
- Yellow and red makes Orange.
- Red and blue makes Violet.
Green, Orange and violet are secondary colors.
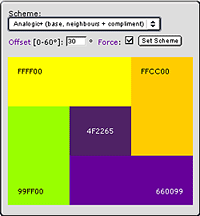
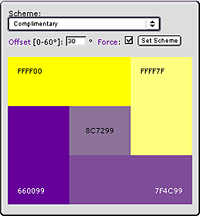
The six tertiary colors are made by combining the primary and secondary colors. (see Fig. 1)
This type of wheel is based on pigment based inks but exists in a computer world. This allows us to 'break' some rules and interpret the wheel differently.